Introduction
Forex market trading, quick for foreign exchange trading, has emerged as a dynamic and complicated economic marketplace that performs a vital role in the worldwide financial system. This comprehensive article will delve into the basics of forex buying and selling, exploring what it means, how it works, and the numerous foreign exchange markets that shape this intricate financial landscape.
Understanding Forex Trading
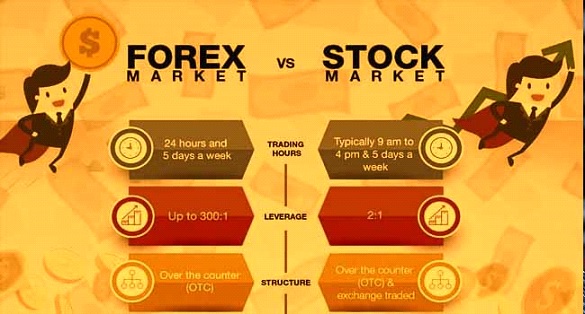
At its core, forex trading includes trading one currency for any other to make a profit. The foreign exchange marketplace operates 24 hours an afternoon, five days a week, and is considered the largest and most liquid global economic market. Participants encompass valuable banks, financial establishments, agencies, and individual buyers.
Currency Pairs
Forex buying and selling revolves around foreign money pairs, wherein one foreign money is exchanged for another. The first currency inside the team is the base foreign money, at the same time as the second is the quote foreign money. The trade charge represents the quantity of the quote forex had to buy one unit of the base currency.
Forex Brokers and Platforms
Individuals usually use foreign exchange agents to participate in foreign exchange trading, which act as intermediaries among investors and the interbank foreign exchange market. The Forex market buying and selling systems furnished via brokers facilitate the execution of trades and offer numerous equipment for evaluation.
Mechanics of the Forex Market Trading
Leverage and Margin
Leverage lets investors play a more significant role with excess capital. While leverage magnifies capability income, it additionally will increase the risk of good-sized losses. Margin is the quantity of money required to open a leveraged position, and traders should keep in mind coping with it to avoid liquidation.
Bid and Ask Prices
The foreign exchange market operates on a bid-and-ask rate system. The bid rate is the highest amount a buyer is willing to pay, whereas the asking price is the lowest price a supplier is inclined to accept. The difference between those two expenses is referred to as the spread.
Market Orders and Limit Orders
Traders can execute market orders on the cutting-edge marketplace fee or area restrict orders to shop for or sell at a selected price. Understanding these order types is critical for robust trade control and danger management.
Types of Forex Markets
Spot Market
The spot forex marketplace includes the direct alternative of currencies at the current market charge. Transactions inside the spot market settle “immediately,” which means within a quick time frame, usually two enterprise days.
Forward Market
In the forward foreign exchange market, contracts are agreed upon for the alternate currencies at a future date and a predetermined charge. This market affords participants with a way to hedge against foreign money fluctuations.
Futures Market
Forex futures involve standardized contracts traded on organized exchanges. These contracts specify the amount, charge, and transport date, presenting apparent and regulated surroundings for forex buying and selling.
Options Market
The Forex market options provide buyers with the proper, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency pair at a predetermined fee inside a targeted time frame. Options offer flexibility and are typically used for hedging techniques.
Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
Effective change management is essential to a hit forex trading. Traders commonly use stop-loss orders to restrict potential losses by mechanically closing a function if the marketplace moves towards them. Conversely, take-earnings orders are set to robotically near a trade while a predetermined profit level is reached.
Risk-Reward Ratio
Traders often compare capacity trades by considering the hazard-reward ratio. This ratio compares the expected profit to the capacity loss, assisting investors in assessing whether or not an exchange is well worth pursuing. Maintaining a favourable risk-reward balance is a crucial factor in danger control.
Diversification
Diversifying a buying and selling portfolio throughout different currency pairs and asset classes can help unfold danger. By avoiding an over-reliance on a single function, traders can lessen the adverse effects of market fluctuations on their whole portfolio. By preventing an over-reliance on a single part, traders can alleviate the negative impact of market fluctuations on their entire portfolio.
Fundamental and Technical Analysis
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental evaluation includes assessing financial signs, geopolitical events, and economic rules to apprehend the forces influencing forex values. Traders examine monetary information, which provides for GDP increase, employment figures, and interest quotes, to make informed trading choices.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis involves reading ancient charge charts and using diverse technical signs to identify capability traits and entry/go-out factors. Popular technical indicators include moving averages, RSI, and MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence).
Economic Indicators and News
Major Economic Indicators
Traders carefully display monetary signs that impact forex values. Key indicators encompass GDP increase, inflation costs, unemployment figures, and central bank hobby fee decisions. Understanding those indicators facilitates buyers’ ability to count on market moves and make knowledgeable choices.
News and Events
Global activities, including elections, alternate agreements, and geopolitical tensions, can extensively affect forex markets. Traders must live informed about applicable information and activities to respond promptly to market developments.
Ongoing Learning and Adaptation
The Forex market buy and sell is a vast field that calls for continuous mastering and variation. Needs evolve, and staying well-informed about new strategies, technology, and market dynamics is essential. Engaging with academic resources, attending webinars, and networking with other traders can contribute to ongoing ability improvement.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the basics of forex trading are essential for everyone venturing into this dynamic monetary realm. Understanding the mechanics of buying and selling, the position of leverage, and the various forms of forex markets empowers individuals to navigate this complicated panorama with self-belief. As with any financial endeavour, thorough training, threat management, and continuous studying are crucial to achievement within the ever-evolving international of forex buying and selling.
FAQs
1. What is Forex Trading?
Forex buying and selling, quick for foreign exchange trading, is the worldwide marketplace for purchasing and promoting currencies. It entails exchanging one foreign money for another to make a profit. The forex marketplace operates 24 hours a day, five days every week, and is the biggest and most liquid financial marketplace globally.
2. How Does Forex Market Trading Work?
Forex trading works through buying and selling currency pairs, exchanging one currency for another. Traders speculate at the rate actions of these foreign money pairs, aiming to take advantage of modifications in alternate prices. The marketplace operates via a community of contributors, such as relevant banks, monetary institutions, groups, and man or woman traders, facilitated by foreign exchange agents and buying and selling systems.
3. What are the Different Types of Forex Market Markets?
There are several styles of foreign exchange markets.
Spot Market: Involves the direct trade of currencies at the contemporary market price, with transactions settling within a brief timeframe.
Forward Market: Involves contracts agreed upon for the exchange of currencies at a destiny date and a predetermined price, providing a manner to hedge against forex fluctuations.
Futures Market: Involves standardized contracts traded on organized exchanges, specifying the quantity, rate, and shipping date.
Options Market: Involves the proper, but not the duty, to shop for or sell a forex pair at a predetermined rate within a particular timeframe.
4. How Can I Manage Risks in the Forex Market Trading?
Risk control in foreign exchange buying and selling is crucial. Traders can implement techniques that include:
Stop-loss and Take-Profit Orders: Setting computerized orders to limit losses and steady profits.
Risk-Reward Ratio: Evaluating potential trades via comparing predicted profit to ability loss.
Diversification: Spreading buying and selling portfolios throughout one-of-a-kind forex pairs and asset training.
5. What Role Does Analysis Play in Forex Trading?
The analysis is essential to informed selection-making in forex buying and selling:
Fundamental Analysis: Involves assessing financial signs, geopolitical events, and economic policies to recognize the forces influencing forex values.
Technical Analysis: Involves studying historic charge charts and using technical indicators to identify trends and entry/go-out factors.
Staying knowledgeable about economic indicators, information, and ongoing learning are critical components of a successful evaluation in the dynamic international of forex buying and selling.