Introduction
While many traders focus on trending markets, another valuable aspect of forex trading should be considered: trading forex ranges.
Understanding Forex Ranges
Forex ranges refer to periods when currency pairs trade within a well-defined price range, characterized by support and resistance levels. During these periods, prices tend to move sideways, making it challenging for traders who rely on trend-following strategies. However, for range traders, this environment provides ample opportunities to profit.
Critical Components of Forex Ranges:
Support and Resistance Levels: These are critical levels where prices bounce off repeatedly. Support is the price level at which demand is strong enough to prevent further price decline, while resistance is the level where selling pressure prevents further price increases.
Range Boundaries: The upper and lower boundaries of the range define the trading limits. Traders look for price bounces at these levels to initiate trades.
Range Width: More comprehensive ranges offer significant profit potential but may carry higher risk.
Trading Strategies for Forex Ranges
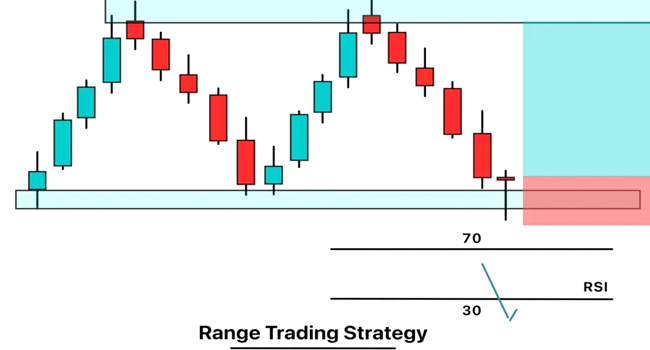
Range Trading Strategy:
Identify a well-defined range on the forex chart.
Buy near the support level and sell near the resistance level.
Pay attention to price patterns, candlestick formations, and technical indicators for additional confirmation.
Breakout Trading Strategy:
Wait for the price to approach the range boundaries.
When a breakout occurs, enter a trade toward the flight.
Mean Reversion Strategy:
Look for instances where the price moves to the end of the range.
Bet on a reversal towards the range’s center or the opposite boundary.
Risk Management in Forex Range Trading
Proper Position Sizing: More minor positions can reduce risk, especially in volatile markets.
Stop-Loss Orders: Always set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Place them outside the range boundaries to give your trade room to breathe.
Diversification: Avoid concentrating all your trading capital in a single currency pair or range. Diversifying your trades can spread risk and enhance your overall portfolio performance.
Use Leverage Wisely: While Leverage can amplify profits, it can also magnify losses. Only use Leverage if you thoroughly understand its risks and have a risk management plan.
Tips for Successful Forex Range Trading
Patience Pays Off: Wait for apparent range formations before initiating trades. Rushing into the market during uncertain conditions can lead to losses.
Keep an Eye on Economic News: Fundamental factors can influence currency prices even within a range. Stay informed about economic releases and events that may impact your chosen currency pair.
Use Technical Analysis: Combine technical indicators like Moving Averages, Bollinger Bands, and MACD with your range trading strategy for added confirmation.
Monitor Multiple Timeframes: Analyzing multiple timeframes can provide a broader perspective on the market, helping you make more informed trading decisions.
Keep Emotions in Check: Emotional trading can lead to impulsive decisions. Stick to your trading plan, and don’t let fear or greed dictate your actions.
Volatility Analysis: Assess the level of volatility within the range. Volatility can impact the effectiveness of your range trading strategy. Fields may be tighter in low-volatility environments and require more precise entries and exits. Conversely, higher volatility might lead to more comprehensive ranges and significant price swings.
Multiple Range Analysis: Rather than focusing on a single range, look for overlapping or nested fields on different timeframes. This can provide more robust trading opportunities, as ranges within ranges often yield strong support and resistance levels.
Time of Day: Be aware of when the forex market experiences the most activity. The overlap between major trading sessions (such as the London and New York sessions) can often lead to increased volatility and clearer range breakouts or reversals.
Correlation Analysis: Analyze the correlation between currency pairs. Some pairs move together or in opposite directions due to economic or geopolitical factors. Understanding these correlations can help you make informed decisions when trading forex ranges.
Pattern Recognition: Beyond standard technical analysis tools, develop your pattern recognition skills. Recognizing recurring chart patterns like triangles, rectangles, and flags can provide additional entry and exit signals within the range.
Market Sentiment Analysis: Keep an eye on market and news sentiment related to the currency pair you’re trading. Sentiment can shift suddenly and lead to range breakouts or reversals. Tools like forex sentiment indicators and news aggregators can assist in staying informed.
Partial Position Management: Instead of entering a full position immediately, consider scaling in or out of a trade. Start with a smaller position size and add to it as the trade moves in your favor. This technique allows you to adapt to changing market conditions more effectively.
Adaptability: Forex markets evolve; ranges can transition into trends or break down altogether. Be prepared to adjust your strategy when necessary. If the content becomes less defined, switching to a different trading approach might be time.
Backtesting: Before implementing advanced techniques, thoroughly backtest them using historical data. This process helps you understand the strategy’s performance under various market conditions and refine it accordingly.
Continuous Learning: Forex trading is a dynamic field, and staying up-to-date with market developments, new trading tools, and advanced techniques is essential for success. Consider joining trading communities, attending webinars, and reading relevant books and articles to continue your education.
Indeed, let’s delve further into some specific advanced techniques and considerations for successful forex range trading:
Using Advanced Indicators:
Bollinger Bands: Conversely, when it comes to the lower band, it may be oversold, indicating a possible move higher.
Keltner Channels: Similar to Bollinger Bands, Keltner Channels offer insights into volatility. When the price touches or breaches the upper channel, it might be time to consider selling, and when it feels or breaches the lower track, it might be an opportunity to buy.
Fibonacci Levels: Fibonacci retracement levels can also be applied to range trading. Look for confluence between Fibonacci levels and support/resistance within the range. These levels can provide strong trade entry and exit points when they align.
Range Expansion Breakout Strategy: Sometimes, a range can break into a new trend. In such cases, you can switch from a range trading strategy to a trend-following process. Use tools like moving averages or trendlines to identify the beginning of a new trend and ride it for potential profits.
News Trading within Ranges: Attention to scheduled economic releases or unexpected news events. These can lead to temporary spikes in price, breaking the range. Consider whether to stay out of the market during such events or take advantage of the increased volatility cautiously.
Market Depth Analysis: Utilize market depth or level II data if available. This can provide insights into the order flow at various price levels, helping you anticipate potential reversals or breakout points within the range.
Avoid Overtrading: In range trading, it’s crucial not to force trades. There may be periods when the market lacks explicit ranges. Sitting on the sidelines and waiting for more favorable conditions is wise during such times.
Psychological Preparation: Successful range trading requires a disciplined mindset. Stick to your trading plan, avoid revenge trading (making impulsive trades after losses), and maintain realistic expectations. Understanding that only some businesses will be profitable is essential for long-term success.
Backward Testing: Besides backtesting historical data, consider “forward testing.” This involves paper trading or a demo account to test your strategy in real time without risking actual capital. This practice helps identify any issues with your system that need to be apparent in historical data.
Adaptive Range Strategies: Develop strategies tailored to different ranges (narrow, wide, horizontal, diagonal, etc.). Adaptability allows you to adjust your approach based on a specific conditions field.
Record Keeping: Maintain a trading journal to record your trades, decisions, and emotions. Reviewing your diary regularly can help you identify areas for improvement and reinforce discipline in your trading.
Conclusion
Forex range trading is a valuable skill that can help traders profit in sideways-moving markets—by understanding the critical components of ranges, implementing appropriate trading strategies, and managing risk effectively.